Edge Computing: Processing Data Closer to the Source in Software
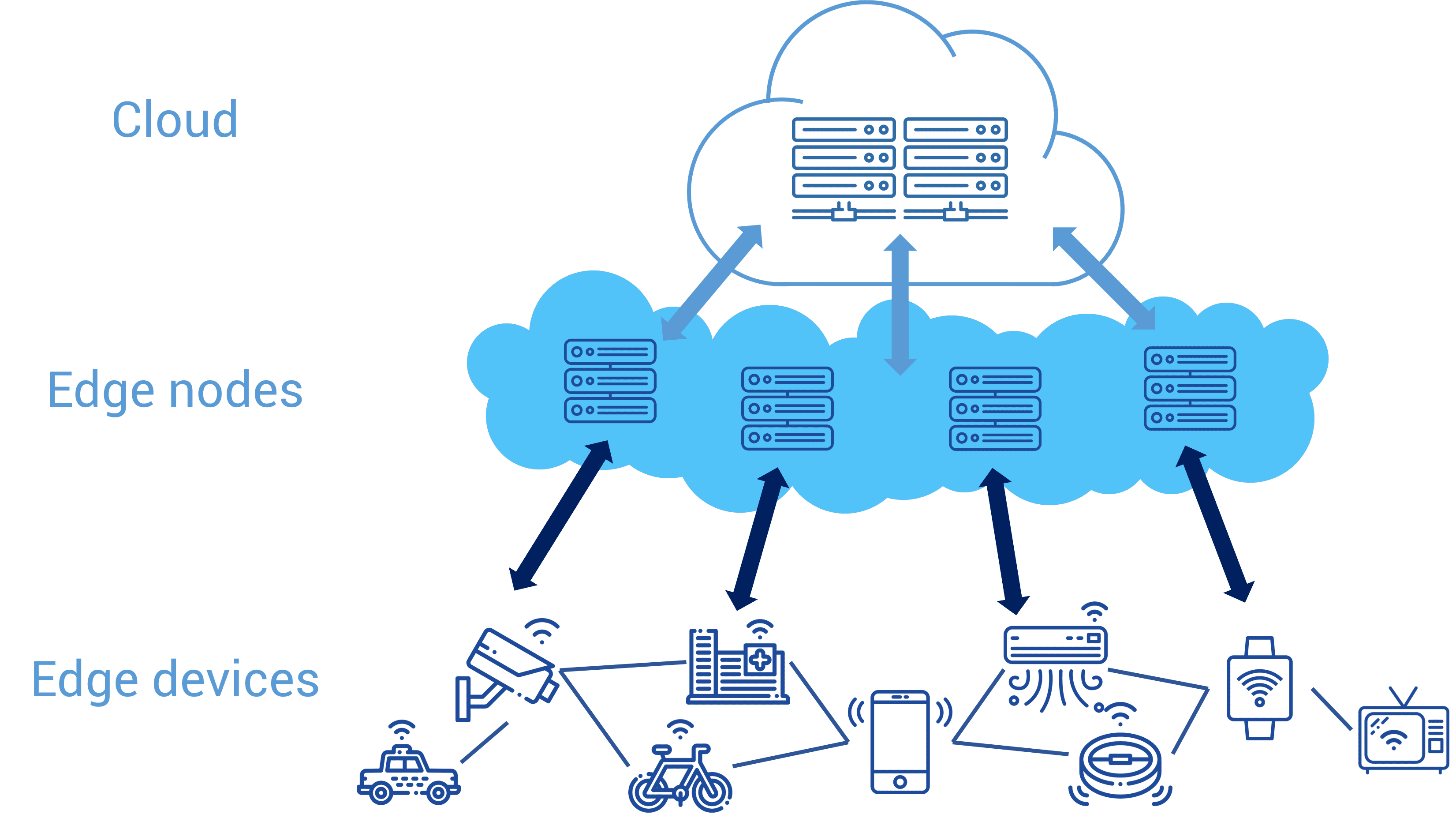
Edge computing is transforming the software landscape by shifting data processing closer to the source of data generation. This paradigm shift addresses latency, bandwidth, and privacy concerns, enabling real-time processing and analysis of data from IoT devices and other sources.
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing and analyzing data at or near the data source, reducing the need for central data centers.
Challenges of Centralized Computing
Centralized computing can lead to latency, bandwidth limitations, and privacy concerns.
Decentralized Processing
Edge computing distributes processing across edge devices, reducing the need for data transmission to central servers.
IoT and Edge Computing
Edge computing is crucial for real-time processing of data from IoT devices.
Reduced Latency
Edge computing reduces latency by minimizing data travel distance, enabling real-time responsiveness.
Bandwidth Optimization
Edge computing optimizes bandwidth usage by transmitting only relevant data to central systems.
Privacy and Security
Edge computing enhances privacy by processing sensitive data closer to the data source.
Scalability and Flexibility
Edge computing allows for scalable and flexible processing based on specific application needs.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
Edge computing is used in autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, healthcare, and more.
Edge Devices and Infrastructure
Edge devices include routers, gateways, and IoT sensors, while edge infrastructure provides computational resources.
Hybrid Approaches
Hybrid edge-cloud architectures combine edge computing with centralized cloud resources.
Future Trends in Edge Computing
Advancements in 5G connectivity, AI, and edge hardware will shape the future of edge computing.
In conclusion, edge computing represents a transformative shift in software development, enabling real-time processing and analysis of data. By leveraging edge computing, developers can create applications that are more responsive, efficient, and capable of handling the data demands of the modern digital landscape.




